Backend Development Services for Saudi & UAE Growth
Backend Development Services for Saudi & UAE Growth

Backend Development Services in GCC: Secure, Compliant Backends for Riyadh, Dubai & Doha
Backend development services design, build and maintain the server-side logic, databases, APIs and integrations that power your web and mobile apps, ensuring they are fast, secure and scalable. In Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Qatar, GCC-ready backend partners also bake in SAMA, TDRA and QCB compliance, local data residency, and Arabic/English support so digital platforms in Riyadh, Dubai and Doha can grow confidently.
Introduction
Across Riyadh, Dubai and Doha, frontends are getting faster and more impressive but many organizations still rely on fragile, legacy backends that were never designed for today’s traffic, integrations and compliance rules. As Saudi Vision 2030, Dubai’s smart city agenda and Qatar’s digital government programs accelerate, these weak foundations are becoming real business and regulatory risks.
Backend development services are about building the “engine room” of your platform: the server-side application development, databases, APIs, security, and monitoring that keep your banking app, e-government portal or ecommerce store running 24/7. For GCC organizations, the right backend development company in Dubai, Riyadh or Doha doesn’t just write code—it understands SAMA, TDRA, QCB, NDMO, DGA and data residency, and designs secure, cloud-native backends that can scale across AWS Bahrain, Azure UAE and GCP Doha.
In this guide, we’ll explain what backend development services look like in the GCC, how modern tech stacks and cloud-native architectures are used, what compliance really requires in Saudi, UAE and Qatar, how a typical project runs, what it costs, and how to choose the right partner.
What Are Backend Development Services in GCC?
Backend vs Frontend in Modern GCC Digital Platforms
Think of your digital platform as a building. The frontend is what users see screens in your banking app, forms on a government portal, product pages on an ecommerce site. The backend is everything behind the scenes: servers, APIs, business logic, security, and data.
Backend development services focus on.
Server-side application development (Node.js, .NET, Laravel, Django, etc.)
Database design and optimization (SQL and NoSQL) for high availability and performance
API integration and development services to connect with payment gateways, government APIs, ERPs and CRMs
Authentication, authorization and identity management
Logging, monitoring, and observability
In KSA, UAE and Qatar, backend stability often matters more than the UI itself. A payment failure on a Riyadh fintech app, a slow Abu Dhabi government portal, or downtime on a Doha telecom self-care app all point back to backend bottlenecks not the screens.
For banks, government portals and telecom apps, a strong backend means:
Reliable transactions even during peak salary days in Jeddah or Dubai
Secure access to citizen services on DGA or Qatar Digital Government platforms
Consistent performance for millions of daily users in Riyadh and Doha
Why Saudi, UAE and Qatar Organizations Rely on Strong Backends
Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Qatar are not just “going digital”; they’re building fully connected economies:
E-government
Platforms driven by DGA in KSA, TDRA-led initiatives in UAE and Hukoomi in Qatar need backends that can integrate with ID systems, payment rails and legacy registries.
Open banking and fintech
SAMA’s open banking framework in Saudi and ADGM/DIFC ecosystems in UAE demand secure, auditable APIs and event-driven architectures.
Ecommerce and retail
Riyadh, Dubai and Doha retailers rely on backends that can handle flash sales, loyalty programs and omni-channel inventory.
Smart cities
From traffic sensors in Abu Dhabi to smart parking in Doha, smart city platforms depend on real-time data ingestion and scalable microservices for enterprise applications.
In reality, this is why “generic outsourcing” from outside the region often fails. A backend that’s fine for a simple US ecommerce site may not survive the combination of Arabic/English UX, national ID integrations, local gateways, and regulator audits in the GCC.
Typical Backend Components in a GCC Project
A typical GCC backend development project includes
APIs & microservices
REST or GraphQL APIs that power mobile apps, portals and partner integrations.
Authentication & authorization
OAuth2, JWT, SSO, integration with national IDs (e.g., UAE Pass, Qatar Digital ID) and enterprise IAM.
Integrations
Banks, Open Banking KSA, SADAD, local payment gateways, ERPs, CRMs, SMS gateways, and telecom APIs.
Arabic/English content handling
Unicode-safe data models, RTL/LTR considerations, search and indexing that work well for both languages.
Audit trails & logging
To satisfy SAMA, TDRA and QCB expectations for traceability and incident investigation.
Monitoring & alerting
Dashboards and alerts for latency, error rates and unusual activity across Riyadh, Dubai, Abu Dhabi and Doha traffic patterns.
When done right, these components work together as a single, secure “platform engine” rather than a collection of fragile scripts.
Core Backend Development Services for Saudi, UAE & Qatar.
Custom API & Microservices Development for GCC Platforms
Modern GCC platforms rarely run on a single monolith. Organizations in Riyadh, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Doha, Kuwait City, Manama and Muscat increasingly prefer:
Microservices for isolated business domains (payments, onboarding, notifications).
Event-driven backends using queues and streams for logistics tracking, fraud detection and real-time notifications.
Well-documented REST/GraphQL APIs to support partners, mobile apps and third-party developers.
Backend development services in Riyadh for enterprise apps often include designing domain-driven microservices around core business capabilities, then exposing them via secure gateways. In the UAE, a backend development company in Dubai for mobile and web apps might prioritize GraphQL for flexible frontends and heavy use of caching for tourism and ecommerce traffic. In Qatar, microservices are frequently used for smart city telemetry and banking APIs.
Backend for Web, Mobile Apps & Omnichannel Experiences
A modern backend should be channel-agnostic. The same backend can (and should) power:
iOS and Android apps for customers in Jeddah, Riyadh, Dubai and Doha
Admin and partner portals for internal teams and B2B clients
Call-center tools and chatbots
Public APIs for partners and fintechs
Key capabilities include
Unified authentication and user profiles
Centralized order, ticket or case management
Consistent Arabic/English messaging across all channels
Rate limiting and throttling to protect core systems
Real GCC scenarios
A Riyadh fintech startup exposes SAMA-compliant APIs to partners while using a shared backend for its consumer mobile app and internal risk dashboard.
A Dubai ecommerce brand uses a single backend to sync inventory across marketplaces, its own website, and in-mall kiosks.
A Doha SME runs its customer portal, mobile app and smart city integration on one backend, deployed in GCP Doha to meet data residency expectations.
Integrations, Legacy Modernization & Support SLAs
Most GCC organizations already have systems in place core banking, legacy CRMs, custom-built government registries, on-prem ERPs. Backend development services often include:
Integration with local CRMs, ERPs and core systems
Payment and billing integrations: SADAD, local gateways, telecom billing systems
Government identity and access: UAE Pass, Qatar Digital ID, DGA services in Saudi
Open Banking KSA, ADGM/DIFC-regulated fintech APIs, QCB guidelines
Legacy modernization typically means.
Wrapping existing systems with secure APIs
Gradually moving to microservices while maintaining business continuity
Introducing CI/CD pipelines and automated testing
To de-risk adoption, serious backend partners offer 24/7 support SLAs, with clear response times, incident handling and regular health checks tailored to mission-critical services in Riyadh, Dubai, Doha and beyond.
GCC Tech Stacks & Architectures for Modern Backends
Node.js & Laravel for GCC Startups and Scaleups
In Saudi and UAE startup ecosystems, Node.js and Laravel (PHP) are extremely popular because they:
Enable fast MVPs and iterations
Have large talent pools in Riyadh, Jeddah, Dubai and Sharjah
Offer great support for real-time APIs, notifications and chat
Fit well with microservices patterns and containerization
For a fintech MVP or ecommerce platform, Node.js-based microservices and a Laravel-based admin panel can deliver speed without compromising security especially when combined with robust database design and optimization across SQL and NoSQL technologies.
NET & Python/Django for Government & Regulated Enterprises
For ministries, banks and telcos, .NET and Python/Django often align better with existing infrastructure and security baselines.
Many government entities in Riyadh, Abu Dhabi and Doha already run Microsoft-centric stacks and Active Directory.
Security teams are familiar with .NET’s hardening practices and tooling.
Python/Django shines for data-heavy, workflow-driven portals and analytics dashboards.
A backend development company in Doha for government and smart city portals might propose Django for administrative portals combined with Python-based data pipelines, while a Saudi bank in Dammam could standardize on .NET for its core APIs and microservices.
From Monoliths to Cloud-Native Microservices
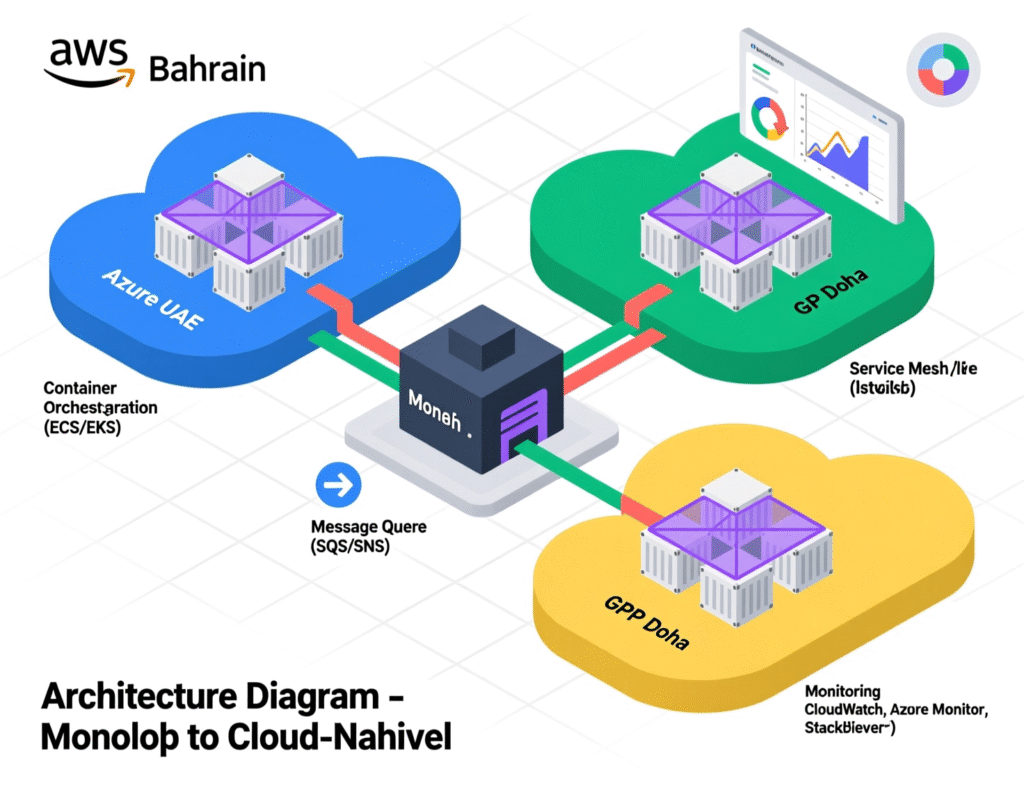
A big part of backend modernization in GCC is moving from single, large monolithic applications to cloud-native backend architecture on AWS, Azure and GCP and regional clouds like Alibaba Cloud Dubai and G42.
Typical migration paths
Assessment
Map current monolith features, integrations, and performance pain points.
Strangling the monolith
Build new APIs and microservices around critical functions (payments, onboarding) and route traffic gradually.
Cloud region alignment
AWS Bahrain for KSA-focused workloads
Azure UAE Central or North for UAE-centric services
GCP Doha for Qatar smart city or banking workloads
Alibaba Cloud Dubai or G42 for specific UAE hosting and AI scenarios
Observability & resilience
Implement tracing, centralized logging, autoscaling and blue/green deployments.
This approach lets organizations in KSA, UAE and Qatar modernize without “big bang” rewrites or risky downtime.
Compliance, Security & Data Residency in Saudi, UAE & Qatar.
Designing SAMA & NDMO-Aligned Backends in Saudi Arabia
Saudi organizations especially in banking, fintech and government must align with SAMA, NDMO and often DGA requirements. Practically, this means:
Data classification (public, internal, confidential, restricted) and mapping each class to correct storage and access controls
Encryption in transit and at rest, with key management in Saudi data centers
Detailed logging and audit trails for all financial and personal data actions
Data residency
Hosting workloads on national cloud providers or Saudi-located regions (e.g., local providers, on-prem DCs, or compliant cloud zones)
AEO Answer How do backend development companies in Saudi Arabia ensure compliance with SAMA, NDMO and local data residency rules?
They start by mapping business processes and data flows to SAMA and NDMO classifications, then design backends that encrypt data, segregate environments, and log every sensitive action. In practice, GCC-ready partners host workloads in Saudi or SAMA-approved environments, implement strong IAM and network segmentation, and maintain audit-ready documentation that aligns with both SAMA and NDMO guidelines.
For Riyadh and Jeddah-based fintechs, this often includes private subnets, VPN or dedicated connectivity to banks, strict role-based access control, and continuous vulnerability management.
TDRA, ADGM & DIFC Expectations for UAE Backends
In the UAE, backend compliance revolves around:
TDRA guidelines for digital government, telecom and data protection
ADGM and DIFC regulations for financial services, digital banks and fintechs
Sector-specific requirements (healthcare, insurance, etc.)
A compliant backend for a Dubai neobank might:
Run in Azure UAE or AWS UAE regions (where applicable) to keep data local
Use hardened APIs with strong authentication and rate limiting
Maintain detailed, exportable transaction logs for regulator queries
Limit cross-border data flows or add appropriate safeguards
For Abu Dhabi government or semi-government entities, alignment with internal security standards and SOC/SIEM integration is usually mandatory.
QCB & Qatar Digital Government Requirements for APIs
In Qatar, QCB and Qatar Digital Government / Hukoomi shape backend and API expectations, especially for banks and public services. Secure backend development services here typically include:
Robust IAM
Fine-grained access control for internal teams, partners and citizens.
Secure API design
Strong authentication (mutual TLS, signed requests), input validation and protection against common attacks.
Auditability
Clear, searchable logs for every critical action especially financial transactions and citizen data access.
Data residency
Preference for hosting in GCP Doha or Qatar-based data centers where feasible.
A backend development company in Doha for government and smart city portals must combine these requirements with integrations into smart city platforms and sensor networks, ensuring citizens enjoy smooth digital services without compromising security.
How a GCC Backend Development Project Runs
From Business Brief to GCC Technical Scope
Every successful backend initiative in the GCC starts with multi-market discovery.
Workshops with stakeholders from Saudi, UAE and Qatar (e.g., Riyadh HQ, Dubai regional office, Doha operations)
Mapping business processes, user journeys and data flows.
Documenting all integration points: banks, gateways, ERPs, government APIs, legacy systems.
Capturing language needs (Arabic/English) and content workflows.
Identifying compliance constraints for SAMA, TDRA, QCB, NDMO, DGA and internal security teams.
The outcome is a clear technical scope and prioritized roadmap, instead of a vague “build us an API.”
Architecture, Prototyping & Cloud Region Selection
Next comes architecture and validation.
Choosing the right stack (.NET, Node.js, Laravel, Python/Django) based on internal skills and regulatory comfort.
Designing architecture diagrams: microservices boundaries, data stores, queues, gateways, security layers.
Selecting cloud regions
AWS Bahrain for KSA-centric workloads
Azure UAE for UAE-centric services
GCP Doha for Qatar workloads
Alibaba Cloud Dubai and G42 for specialized UAE scenarios
Building prototypes or proof-of-concept APIs to validate performance, security and integrations early.
This is where you also decide how much of the monolith to keep, and how aggressively to move toward cloud-native backend architecture.
Development, Testing, Go-Live & 24/7 Support
Once architecture is set, development moves through a structured lifecycle.
Development & CI/CD:
Iterative sprints, automated tests, code reviews, and pipelines that deploy to staging and production.
Testing
Functional, integration, performance and security testing (including penetration tests) tuned to Riyadh, Dubai and Doha traffic patterns.
Go-live
Carefully planned cutovers or phased rollouts, with rollback strategies and joint war-room monitoring.
Support & optimization
24/7 SLAs, regular health checks, performance tuning, security updates, and continuous feature delivery.
For government portals and fintech apps, this stage is where SLAs, incident management processes and regulator-ready reporting are truly tested.
Backend Development Costs & Engagement Models in KSA, UAE & Qatar
Typical MVP and Phase-1 Cost Ranges by Country
Costs vary widely depending on scope, integrations and regulatory depth, but some patterns are consistent:
A small to mid-sized MVP backend for a fintech, ecommerce or logistics startup may range (very broadly) from low five figures to low six figures (USD equivalent) across Saudi, UAE and Qatar.
Saudi projects with SAMA/NDMO requirements often cost more due to security, data residency and audit expectations.
Integrations with core banking, multiple ERPs or complex smart city platforms can significantly increase effort.
AEO Answer How much do backend development services cost in Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Qatar for a typical MVP?
Most GCC-ready backend MVPs in Saudi, UAE and Qatar fall into a broad low five- to low six-figure USD-equivalent range, depending mainly on complexity, integrations and regulatory scope. Saudi projects under SAMA/NDMO oversight and UAE/Qatar fintech or smart city projects typically cost more than simple ecommerce or content platforms because of security, testing and compliance requirements.
Fixed-Price Projects vs Dedicated Backend Teams
Two engagement models dominate GCC backend work:
Fixed-price projects
Best for well-defined scopes and clear deadlines (e.g., Phase-1 of a Riyadh loyalty platform).
Easier for government and semi-government procurement in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Doha and Dammam.
Less flexible for change requests; scope creep can be painful.
Dedicated backend teams
Ideal for evolving products: fintech platforms, gov portals, logistics stacks.
More transparent capacity and long-term knowledge retention.
Works well when product owners in Riyadh, Dubai or Doha run continuous backlogs and experiments.
Many enterprises use a hybrid: fixed-price for initial rollout, then dedicated squads for continuous improvements.
Outsourcing vs GCC-Based Backend Partners
While offshore outsourcing can look cheaper on paper, many GCC organizations now favor GCC-based backend partners because they
Understand SAMA, TDRA, QCB, NDMO, DGA and local procurement norms.
Work within similar time zones, enabling real-time collaboration with Riyadh, Dubai and Doha teams.
Design for Arabic UX and local payment behaviors from day one.
Are more familiar with AWS Bahrain, Azure UAE, GCP Doha and regional clouds.
For critical systems, the cost of fixing a compliance misstep or production incident often outweighs any short-term savings from purely offshore teams.
How to Choose the Right Backend Development Company in Riyadh, Dubai or Doha
GCC-Focused Checklist for Evaluating Backend Vendors
When shortlisting backend partners in Riyadh, Dubai, Abu Dhabi or Doha, look for:
Regulatory experience
Proven projects under SAMA, TDRA, QCB, NDMO, DGA, ADGM or DIFC oversight.
Cloud certifications
AWS, Azure, GCP and regional cloud expertise, especially in Bahrain, UAE and Qatar regions.
Arabic/English UX understanding
Not just translation actual bilingual content flows and RTL/LTR handling.
Relevant case studies
Fintech, government, smart city, ecommerce or logistics work in KSA, UAE, Qatar or wider GCC.
Security mindset
Secure coding practices, penetration testing, DevSecOps, and integration with your SOC/SIEM where needed.
A strong backend development company in Dubai for mobile and web apps should be able to point to live platforms across multiple GCC markets not just generic global references.
Questions to Ask About Security, Compliance & Data Residency
In your RFPs and vendor interviews, ask.
Where exactly will our data be stored (country, region, provider)?
How is data encrypted (at rest, in transit, key management)?
What IAM model will you use—roles, privileges, and approval workflows?
How do you log and monitor critical actions, and who has access to logs?
What is your incident response process and SLA for security issues?
How have you previously aligned with SAMA/NDMO, TDRA, QCB or internal security frameworks?
The best partners will answer confidently, with concrete examples not vague promises.
Kick-Starting a GCC-Ready Backend Project
If your backend is struggling to keep up with new features, traffic or compliance demands, the right first step is usually a backend health check. That means reviewing architecture, code quality, security posture and cloud deployment across your Riyadh, Dubai and Doha environments.
From there, you can define a roadmap: quick wins, high-impact refactors, and a longer-term move toward cloud-native, microservices-based platforms that fully respect GCC regulations and data residency.
If you’re leading a digital initiative in Saudi Arabia, the UAE or Qatar and need backend development services that truly understand GCC realities, you don’t have to guess your way forward. The Mak It Solutions team can help you review your current architecture, prioritize risks, and design a secure, compliant roadmap aligned with SAMA, TDRA, QCB and your internal governance.
Reach out to Mak It Solutions today to schedule a discovery workshop, request a backend health check, or explore a tailored GCC-ready backend strategy for your bank, government entity, fintech, logistics platform or ecommerce brand. ( Click Here’s )
FAQs
Q : Is it better to host my backend in Saudi, UAE or another region when serving GCC customers?
A : For regulated workloads especially in finance, government and telecom—it’s usually safer to host in-country or at least in-region. Saudi organizations often prefer Saudi-based data centers or AWS Bahrain to stay close to SAMA and NDMO expectations, while UAE entities use Azure UAE or local cloud providers aligned with TDRA guidance. Qatar projects, particularly under QCB or Qatar Digital Government, increasingly favor GCP Doha or Qatar-based hosting. Non-regulated workloads may use broader regions, but legal and security teams should always weigh data residency and cross-border transfer implications.
Q : Can a backend development company in Dubai work on Saudi government or SAMA-regulated projects?
A : Yes many Saudi organizations work with backend partners in Dubai, Abu Dhabi or Sharjah, as long as they understand SAMA and NDMO requirements and can meet data residency rules. In practice, this often means hosting workloads in Saudi-based environments while the delivery team sits in the UAE, with strict controls around access, VPNs, and audit trails. When evaluating a Dubai-based partner, ask for concrete SAMA-aligned case studies and confirm how they handle secure access to Saudi environments. Coordination with Saudi regulators and internal security teams is critical.
Q : How do GCC-ready backend services handle Arabic and English content in one system?
A : Well-designed GCC backends treat language as a first-class concern, not an afterthought. They use Unicode-safe schemas, avoid hard-coded text in code, and store content in localization-friendly formats with clear keys for Arabic and English. Search indices are tuned for both languages, and APIs expose language-aware fields so frontends can render RTL/LTR correctly in Riyadh, Dubai, Doha and beyond. Many teams also integrate with translation workflows and CMS tools so non-technical content teams can manage Arabic/English content without developer intervention, in line with DGA or TDRA digital experience expectations.
Q : What security certifications or standards should a backend development partner have in KSA, UAE and Qatar?
A : While requirements vary by sector, it’s wise to look for partners familiar with ISO 27001, SOC 2, OWASP best practices, and any sector-specific rules you face. In Saudi Arabia, a strong track record under SAMA and NDMO-aligned environments is a major plus; in the UAE, experience with TDRA, ADGM or DIFC-regulated entities signals maturity; in Qatar, prior work with QCB or Qatar Digital Government is valuable. Even if the partner doesn’t own the certification themselves, ensure they can design and document backends that help your organization pass audits against these standards.
Q : How long does a typical backend project for a fintech or government portal take in Riyadh, Dubai or Doha?
A : Timelines depend heavily on scope and integrations, but many GCC fintech and government backend projects run from 3–6 months for an MVP to 9–18 months for large, multi-phase programs. A Riyadh-based fintech connecting to multiple banks under SAMA rules or a Dubai government portal integrating with UAE Pass and legacy registries will require more time for security reviews, testing and regulator feedback. In Doha, smart city or QCB-regulated platforms may add sensor integrations or complex reporting. A good backend partner will phase delivery, so you see value early while still building toward a robust long-term platform.