5G Business Opportunities in the Middle East for GCC
5G Business Opportunities in the Middle East for GCC

5G Business Opportunities in the Middle East for GCC
5G business opportunities in the Middle East are shifting from consumer hype to real value for GCC companies, from smart factories and logistics to stadiums, banks and government services. For Saudi, UAE and Qatar organisations, 5G enables ultra-low-latency IoT, richer mobile experiences and secure data residency by combining operator 5G networks with regional cloud and private 5G options.
Across Saudi Arabia, the UAE and Qatar, 5G networks are no longer pilots they are nationwide assets. Saudi Arabia already enjoys very high 4G/5G availability, while the UAE has ranked among the world’s fastest 5G markets, giving businesses serious bandwidth and reliability to work with.Qatar’s CRA has pushed operators to deploy 5G across densely populated areas and World Cup stadiums, making Doha and Lusail strong testbeds for advanced services.
For GCC decision-makers in Riyadh, Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Doha, Jeddah and beyond, 5G business opportunities in the Middle East for GCC companies now come down to practical questions: which use cases to prioritise, what to keep on public 5G, when to invest in private networks, and how to stay compliant with SAMA, TDRA, QCB and data residency rules.
Quick GCC answer in plain language
5G in the GCC lets businesses connect thousands of devices with ultra-low latency, analyse data in near real time and offer Arabic-friendly digital services to customers and field teams. For most SMEs, operator 5G business packages will be enough, while large factories, ports, oil & gas sites and smart city projects will increasingly mix private 5G with AWS Bahrain, Azure UAE Central and GCP Doha regions for compliant, low-latency cloud.
5G in the Middle East: Why GCC Businesses Should Care Now
From 4G to ultra-low latency 5G networks in the GCC
For many executives, the jump from 4G to 5G feels technical but the impact is commercial. 4G gave the region mobile apps and e-commerce; ultra-low latency 5G lets you remotely monitor machines in Jubail, stream 4K video from a maintenance drone over NEOM, or run AR support in a Dubai warehouse, all in real time.
In practice, that means.
Millisecond-level response for IoT and automation
Higher device density per square kilometre (perfect for factories, ports and stadiums)
Better support for mission-critical services like digital banking, health and public safety
For the wider GCC Kuwait City, Manama, Muscat this is also a chance to plug into regional 5G corridors being built across operators and submarine cables, not be left behind.
How 5G coverage and investment differ in Saudi Arabia, UAE and Qatar
Saudi Arabia (KSA)
STC, Mobily and Zain have invested heavily in 5G coverage, supporting Vision 2030 goals for smart government, fintech and Industry 4.0. Saudi enjoys very high 4G/5G availability, which makes 5G a realistic backbone for national-scale services.
UAE
Etisalat by e& and du compete aggressively on speed and indoor coverage, with Abu Dhabi among the world’s fastest 5G capitals and TDRA pushing a “Digital UAE” vision.
Qatar
Ooredoo and Vodafone, under CRA licences, rolled out 5G across dense urban areas and all key sports venues, including Lusail Stadium, positioning Qatar as a hub for 5G-enabled events and media.
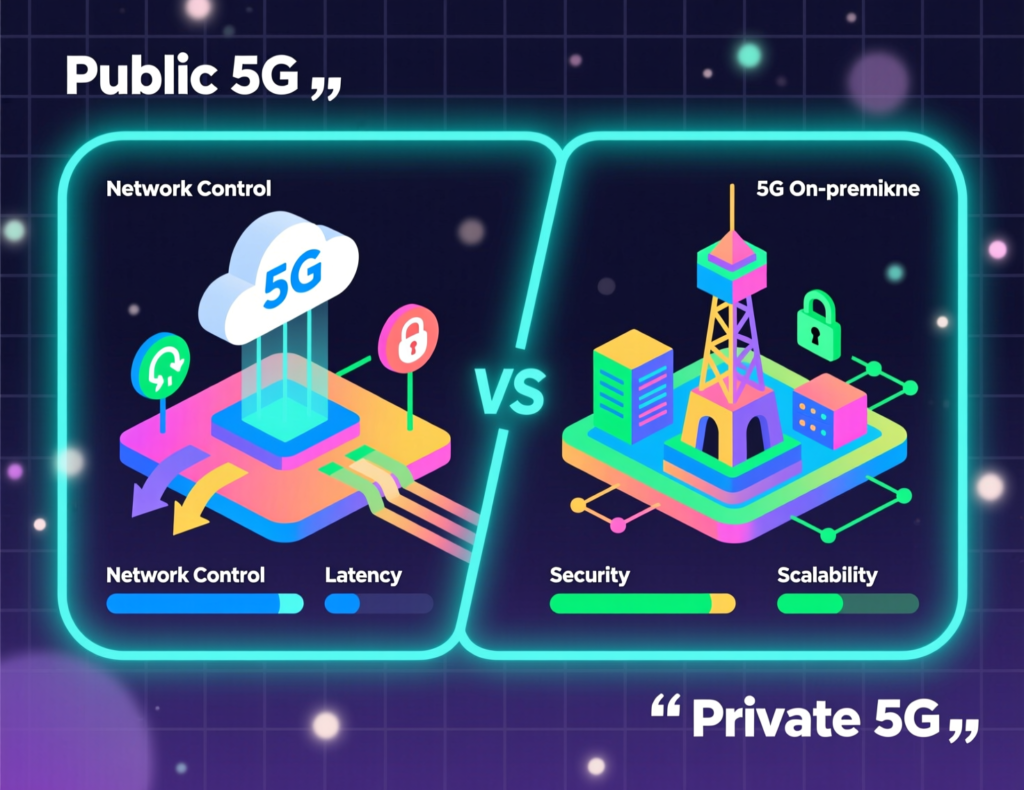
Public 5G vs private 5G in the Middle East at a glance
Public 5G
Delivered by operators like STC, Mobily, Zain, e&, du and Ooredoo. Best for SMEs needing fast business internet, SD-WAN, IoT connectivity and mobile apps across cities and even across borders.
Private 5G
Dedicated network on a factory, campus, port or mega project often integrated with edge computing and on-premises data centres. Ideal for oil & gas, heavy industry, airports, smart ports and sensitive government workloads.
Most GCC organisations will end up using a hybrid model, mixing public 5G, private 5G and secure connections to regional cloud regions such as AWS Bahrain (me-south-1), Azure UAE Central and Google Cloud’s Doha region for compliant data residency.
New 5G Business Opportunities for Startups and SMEs in Saudi, UAE and Qatar
Saudi 5G business use cases under Vision 2030
Vision 2030 is driving digital adoption from fintech to tourism. For startups and SMEs in Riyadh, Jeddah and NEOM, 5G opens doors to:
Real-time logistics tracking using 5G-enabled IoT sensors
Fintech apps that rely on low-latency connections to Open Banking KSA, SADAD and mada
Smart retail and tourism experiences in places like AlUla and Red Sea projects
What business opportunities does 5G create for startups in Saudi Arabia and the wider Middle East?
5G lets Saudi and Middle East startups build always-connected services like instant credit scoring at the point of sale, telemedicine in remote towns or live AR property tours without owning complex infrastructure. When combined with cloud analytics and SAMA/NDMO-aligned data practices, these services can scale from local pilots in Riyadh to regional rollouts across the GCC.
5G for startups and SMEs in Dubai, Abu Dhabi and other UAE hubs
Dubai and Abu Dhabi are already running 5G-ready initiatives through Digital Dubai, ADGM, DIFC and UAE Pass, making life easier for founders. Startups in free zones can:
Launch 5G-powered mobile apps for e-commerce, travel and govtech, built by partners like Mak It Solutions’ mobile app development team
Integrate 5G with UAE Pass for secure identity, enabling instant onboarding and KYC
Use 5G for real-time video support, field-force apps and VR/AR experiences in malls and attractions
5G for businesses in Qatar, Doha and Lusail innovation districts
Qatar’s focus on events and sports World Cup venues, Lusail City, Education City creates space for SMEs to:
Build 5G-enhanced fan engagement apps and smart ticketing
Offer intelligent transport and shuttle services connected via 5G IoT
Provide B2B analytics and CCTV-as-a-service to stadiums, hotels and retail
TASMU Smart Qatar programmes and Qatar Digital ID help align these 5G use cases with national smart city and digital government strategies.
High-Value 5G Use Cases for Enterprises in the GCC
Industry 4.0 and 5G in Saudi and UAE smart manufacturing
For manufacturers in Riyadh’s industrial zones or Abu Dhabi’s KIZAD, Industry 4.0 and 5G in Arab Gulf economies means.
Wireless robots and AGVs in plants, avoiding cabling limits
5G-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) for businesses to track machine health and run predictive maintenance
Digital twins running in Azure UAE or AWS Bahrain, fed by live 5G data
Companies can link these capabilities with business intelligence solutions to visualise performance for plant managers in Arabic and English dashboards.
5G for logistics, smart ports and airports in Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Jeddah and Doha
Ports and airports are perfect for ultra-low latency networks in the GCC. Examples include:
5G-enabled port operations like Qatar’s Hamad Port pilot, where 5G supports cranes, sensors and yard management
Smart baggage handling, asset tracking and turnaround optimisation at Dubai and Abu Dhabi airports
Jeddah Islamic Port and King Abdulaziz Port using 5G to monitor container flows and yard safety

5G for smart cities, mega projects, stadiums and events in NEOM, Expo City Dubai and Lusail
Mega projects such as NEOM and The Line, Expo City Dubai and Lusail City are designed around dense connectivity. 5G supports:
Smart lighting, surveillance and environmental monitoring
Seamless ticketing, crowd analytics and in-stadium AR experiences
Connected maintenance teams using Arabic-friendly mobile apps built on custom web development and PHP/Laravel backends
What are the most common 5G use cases for enterprises in the UAE and GCC (manufacturing, logistics, oil & gas)?
In the UAE and wider GCC, manufacturers use 5G for smart factories and quality monitoring; logistics and ports for fleet tracking, crane automation and yard optimisation; and oil & gas operators for remote asset monitoring, worker safety wearables and real-time video from remote sites. These use cases typically combine operator 5G, private campus networks, edge computing and strong security aligned with SAMA, TDRA and QCB expectations.
Public 5G vs Private 5G Networks for GCC Companies
When public 5G business packages are enough for SMEs in KSA, UAE and Qatar
If you’re an SME in Riyadh, Sharjah or Doha, public 5G is usually enough when:
Your main need is reliable, fast internet and VPN for offices and branches
You’re running cloud-based CRM, ERP or e-commerce platforms
You want affordable SD-WAN and IoT SIMs without managing radio infrastructure
Operators like STC, e&, du and Ooredoo already sell business 5G bundles, which can be paired with website and e-commerce development to monetise your online presence.
5G private networks in the GCC for factories, oil & gas and campuses
Private 5G makes sense when.
You run a critical facility (refinery, airport, port, mine, mega construction site)
You need deterministic performance, strong SLAs and full on-site coverage (including deep indoor)
Data must stay on-prem or in-country to meet SAMA, TDRA or QCB rules
These networks often integrate with industrial systems and on-site edge servers, designed in partnership with system integrators and cloud providers.
Network slicing, SLAs and integration with cloud / IoT platforms
Network slicing lets operators carve out virtual “lanes” on shared 5G infrastructure: one slice for public traffic, another with enterprise-grade latency and reliability. As 5G standalone (SA) enterprise services in MENA mature, expect:
Dedicated slices for banks, public sector, utilities and emergency services
Tight integration with IoT platforms, analytics and web dashboards
Stronger SLAs around latency, uptime and lawful intercept requirements
How can Saudi, UAE and Qatar companies choose between public 5G and private 5G networks?
Start with your risk profile: SMEs and service businesses usually start on public 5G business packages with VPNs and SD-WAN; heavy industry, oil & gas and national infrastructure should evaluate private 5G or dedicated slices to guarantee uptime, coverage and compliance. Then map data residency (SAMA, TDRA, QCB), operational criticality and budget if downtime or a breach would be catastrophic, a private or hybrid 5G model is usually safer.

Regulation, Data Residency and 5G Readiness in KSA, UAE and Qatar
Saudi 5G regulation, CST spectrum policy and SAMA / NDMO data rules
In Saudi Arabia, CST allocates 5G spectrum and oversees telecom performance, while SAMA and the National Data Management Office (NDMO) shape financial and data governance rules. Banks, fintechs and critical infrastructure providers deploying 5G must:
Respect data residency, keeping sensitive workloads inside KSA or approved regional clouds
Ensure lawful intercept and security monitoring for 5G traffic
Align APIs and analytics platforms with SAMA cybersecurity and NDMO classification frameworks
TDRA 5G guidelines, UAE Pass and free-zone considerations in Dubai and Abu Dhabi
TDRA regulates 5G policy and type approval in the UAE, issuing technical standards for 5G devices and supporting a broader “Digital UAE” strategy. ([tdra.gov.ae][6]) In practice, UAE enterprises combining 5G with UAE Pass, Digital Dubai services, ADGM or DIFC frameworks need to:
Check what data can leave UAE borders vs what must stay in-country
Align telecom use with sector rules from the UAE Central Bank and free-zone regulators
Protect national critical infrastructure (transport, utilities, health) handled over 5G networks
Qatar CRA 5G framework, QCB expectations and TASMU smart city programmes
Qatar’s CRA licenses 5G spectrum and mandates coverage for key urban and event venues. QCB supervises banking and fintech, expecting strong controls over 5G-enabled payment and trading platforms. With TASMU Smart Qatar, ministries and enterprises are encouraged to:
Use 5G to connect smart buildings, traffic systems and public services in Doha and Lusail
Host sensitive data in-country or via GCP Doha / regional cloud with clear residency guarantees
Meet cybersecurity standards for smart stadiums, fan zones and hospitality clusters
How 5G Powers Digital Transformation and Industry 4.0 in the Arab Gulf
5G-enabled Internet of Things (IoT) for businesses across the GCC
Across the GCC, 5G-enabled IoT lets businesses connect fleets, equipment and buildings in real time. Examples:
Cold-chain logistics between Jeddah and Manama
Smart building management in Dubai and Sharjah
Remote asset monitoring in Oman’s oilfields
Combined with business intelligence dashboards, this telemetry supports predictive maintenance, energy optimisation and automated alerts.
Why 5G standalone (SA) matters for advanced enterprise services in MENA
Most early networks were “non-standalone”, anchored on 4G cores. As operators roll out 5G standalone (SA) enterprise services in MENA, enterprises gain.
True network slicing for regulated sectors
Lower, more predictable latency for machine-to-machine workloads
Easier integration with edge computing in AWS Bahrain, Azure UAE Central and GCP Doha
This is crucial for ultra-reliable use cases like remote surgery, autonomous vehicles in ports or real-time control of grid infrastructure.
Designing Arabic-friendly 5G applications and customer journeys
For GCC users, Arabic-first UX is not a nice-to-have it’s critical. 5G applications should:
Support Arabic interfaces and right-to-left layouts
Offer bilingual experiences for mixed workforce teams
Integrate with WhatsApp, SMS and call centres that many citizens still prefer
Here, 5G is the enabler; you still need thoughtful UX, performant web and app development and culturally aware customer journeys.
Practical Next Steps for GCC Companies Exploring 5G
How to prioritise 5G use cases and build an internal business case
Map pain points
Identify where latency, connectivity gaps or manual processes hurt factory lines, truck fleets, customer support.
Match to 5G capabilities
Link these pains to 5G benefits (IoT, bandwidth, mobility)
Quantify ROI
Estimate impact on downtime, labour, throughput or new revenue.
Check compliance
Validate SAMA, TDRA, QCB and internal risk requirements early.
Choosing between operators, cloud providers and system integrators in Saudi, UAE and Qatar
Shortlist operators (STC, Mobily, Zain, e&, du, Ooredoo) based on coverage in your actual sites
Align cloud strategy with AWS Bahrain, Azure UAE or GCP Doha for data residency and latency
Bring in a system integrator or specialist partner like Mak It Solutions to design architecture, build dashboards and integrate existing systems
Launching a 5G pilot in Riyadh, Dubai or Doha and scaling across the GCC
Start small
One factory, port terminal, warehouse or smart building.
Define KPIs
Downtime, throughput, incident response, customer NPS.
Co-design with users
Field technicians, plant managers, customer-service teams.
Govern
Create a joint steering committee (IT, OT, risk, business).
Scale
Roll out successful patterns to other cities (Jeddah, Abu Dhabi, Lusail) with standard templates and shared platforms.
If you’re a decision-maker in Saudi Arabia, the UAE or Qatar, 5G is no longer a “future topic” it’s part of today’s digital infrastructure. The question is not whether to use 5G, but where to start and how to stay compliant while delivering real ROI.
Mak It Solutions can help you design 5G-ready web platforms, mobile apps, analytics dashboards and integration layers tailored for GCC regulations, Arabic UX and your sector’s realities. Reach out to our team to explore a practical 5G roadmap, pilot ideas in Riyadh, Dubai or Doha, and build a scalable digital foundation for the next de cade of 5G business opportunities in the Middle East.( Click Here’s )
FAQs
Q : Is 5G business internet available for SMEs outside Riyadh, Jeddah, Dubai and Doha?
A : Yes. In most GCC countries, operators are extending 5G business internet beyond capital cities into secondary cities and industrial zones. In Saudi Arabia, CST reports high 4G/5G availability across much of the Kingdom, not only in Riyadh and Jeddah, reflecting Vision 2030 connectivity goals. ([Opensignal][1]) In the UAE, TDRA’s Digital UAE strategy supports broader 5G reach, while in Qatar the CRA has mandated coverage across densely populated areas. SMEs in places like Dammam, Sharjah and Al Wakrah should still check local coverage maps and indoor signal quality before signing long contracts.
Q : How much does a 5G private network typically cost for a factory in a Saudi or UAE industrial zone?
A : Costs vary widely, but a serious 5G private network is usually a multi-year, multi-million SAR/AED investment once radio equipment, spectrum arrangements (if needed), edge servers, integration and support are included. Large factories in Jubail or Abu Dhabi’s industrial zones often start with a limited pilot cell, then scale coverage site-wide as ROI is proven. To stay aligned with Vision 2030 and UAE industrial strategies, many companies co-invest with operators or vendors instead of trying to own everything themselves, and they phase deployments over three to five years.
Q : Can Saudi and UAE companies host 5G application data in regional clouds and still meet SAMA or TDRA data residency rules?
A : Often yes, if the right regions and controls are used. Many regulated workloads can be hosted in AWS Bahrain, Azure UAE Central or other GCC-adjacent regions with strong contractual and technical safeguards. SAMA and TDRA focus on data classification, localisation of sensitive data, encryption and access control — not banning cloud outright. Companies should map which data must stay in-country versus what can be processed regionally, use encryption and key management carefully, and document architectures so regulators and internal audit can clearly see how 5G data flows.
Q : How can GCC logistics and port operators integrate existing IoT platforms with new 5G networks?
A : Logistics and port operators typically keep their existing IoT platforms for fleet, yard or container tracking and add 5G as a new connectivity layer. This can mean upgrading device modems, adding 5G routers at key sites and configuring APNs or private network access with operators. In Qatar, 5G-enabled ports like Hamad Port show how container terminals can phase in 5G alongside existing Wi-Fi and fibre links. ([Developing Telecoms][5]) Similar approaches are emerging in Jebel Ali and Jeddah, where 5G is introduced first to high-impact zones before being extended across the entire port.
Q : Are there Arabic-friendly 5G apps and dashboards for field teams and technicians in the Middle East?
A : Yes, and the number is growing quickly. Many GCC organisations build custom Arabic/English mobile apps and web dashboards for technicians, drivers and inspectors, running over 5G for live video, work orders and navigation. National initiatives like Saudi Vision 2030 and Digital Dubai encourage Arabic-first digital services, while tools such as UAE Pass and Qatar Digital ID simplify authentication. By pairing 5G connectivity with tailored UX and strong integration work from partners such as Mak It Solutions, companies can give field teams consumer-grade experiences that truly match how they work.